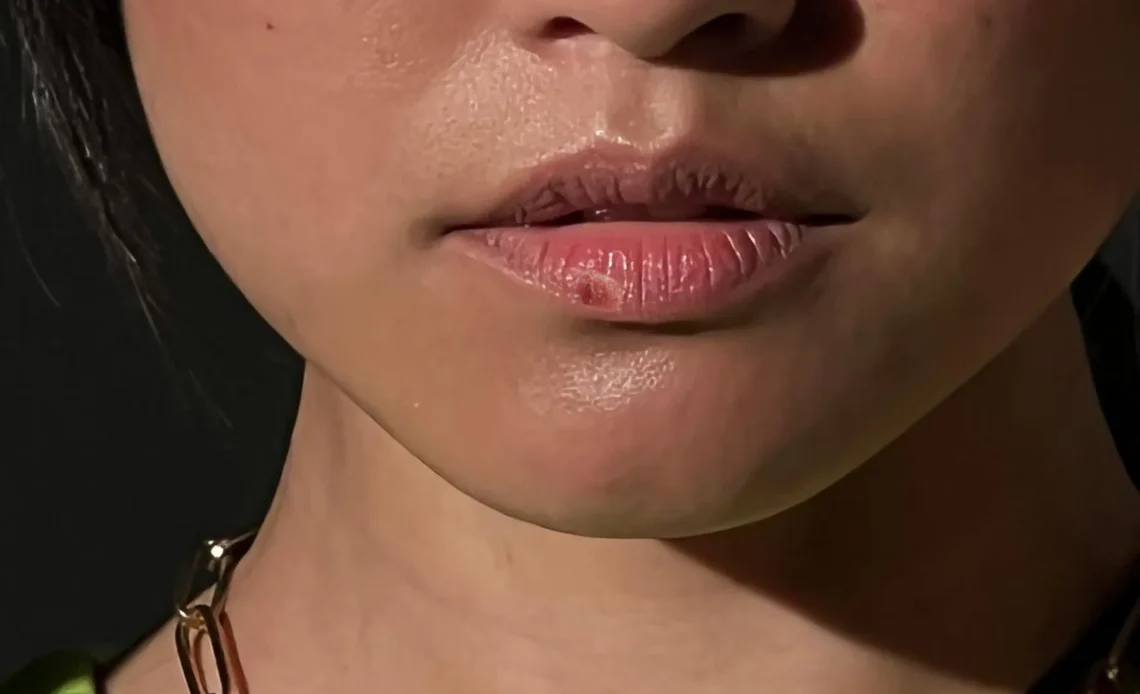Herpes, a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI), affects millions of people worldwide. It manifests as blisters around the mouth or genitals, caused by two main types of viruses: HSV-1 and HSV-2. This article delves into the complexities of herpes, exploring its various forms, symptoms, transmission, diagnosis, and management strategies.
Types of Herpes and Impact
- Oral Herpes (HSV-1): The American Sexual Health Association estimates that roughly half of all adults in the United States carry HSV-1. It’s often the culprit behind cold sores – those pesky blisters that appear around the mouth and lips. While some individuals experience no symptoms, others might face recurring outbreaks triggered by stress, illness, or sun exposure. These sores typically cause tingling, stinging, or burning sensations and can be painful when eating or drinking. Thankfully, they usually clear up within a few weeks.
- Genital Herpes (HSV-1 or HSV-2): This STI spreads through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It’s crucial to remember that both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can cause genital herpes, although HSV-2 is more commonly associated with it. Transmission is more likely from male to female due to anatomical differences. The initial outbreak of genital herpes can be quite unpleasant, featuring flu-like symptoms alongside the characteristic blisters on the genitals. These blisters can be accompanied by itching, pain, and burning during urination, especially if the urine comes into contact with the sores. However, some outbreaks can manifest as seemingly harmless pimples, ingrown hairs, or even yeast infections, making them easily overlooked.
Living with Herpes: Symptoms and Complications
The unpredictability of herpes outbreaks can be a source of frustration. Symptoms typically appear within two weeks of exposure, with the first outbreak often being the most severe. It’s not uncommon to experience flu-like symptoms followed by a tingling or itching sensation around the genitals or mouth before the blisters erupt. The good news is that subsequent outbreaks tend to be milder and shorter in duration.


One of the most concerning aspects of herpes is its contagious nature. The virus can be transmitted even in the absence of visible sores, highlighting the importance of open communication with sexual partners. Early diagnosis and management with the help of a healthcare provider are crucial. A healthcare professional can provide valuable information on managing the condition and minimizing the risk of transmission.
Triggers and Risk Factors
While the exact reasons behind herpes outbreaks remain under investigation, certain factors seem to play a role:
- Stress: Feeling overwhelmed or under pressure can trigger an outbreak.
- Illness: A weakened immune system due to illness can make you more susceptible to outbreaks.
- Fatigue: When your body is depleted, it may be less equipped to fight off the virus.
- Friction in the Genital Area: Tight-fitting clothing or vigorous sexual activity can irritate the genital area, potentially triggering an outbreak.
- Sun Exposure: For individuals with oral herpes, prolonged exposure to sunlight can trigger outbreaks around the mouth.
Diagnosis and Testing
Herpes treatment involves a strategic approach that focuses on minimizing the impact of the virus on daily life. Antiviral medications and supplements, often prescribed by healthcare professionals, play a crucial role in controlling outbreaks. These Herpes supplements are designed to suppress the virus’s replication process, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of outbreaks.

Treatment Options
Herpes treatment involves a strategic approach that focuses on minimizing the impact of the virus on daily life. Antiviral medications and supplements, often prescribed by healthcare professionals, play a crucial role in controlling outbreaks. These Herpes supplements are designed to suppress the virus’s replication process, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Living with Herpes: Maintaining Wellbeing
Beyond medication, several self-care practices can help manage herpes symptoms during outbreaks:
- Maintain Cleanliness: Keeping the affected area clean and dry helps prevent secondary infections and promotes healing.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Opt for loose-fitting, breathable clothing, especially around the genitals, to minimize irritation.
- Prioritize Rest: Getting enough sleep allows your body to focus on healing and fighting off the virus.
- Manage Stress: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels, potentially reducing the frequency of outbreaks.
Coping with the Emotional Impact
A diagnosis of herpes can evoke a range of emotions, including anxiety, shame, and fear of intimacy. Remember, you are not alone. Herpes is a very common condition, and there are resources available to help you cope emotionally. Talking to a therapist or counselor can be incredibly helpful in processing your emotions and developing healthy coping mechanisms. Additionally, support groups can connect you with others who understand what you’re going through.

Building Healthy Relationships
- Choose the right time and place: Pick a private, calm setting where you can have a confidential conversation.
- Be prepared: Gather information beforehand so you can answer any questions your partner might have. e.g. risk factors, diagnose treatments.
- Focus on facts: Present the information factually and avoid blaming yourself or your partner.
- Express your feelings: Let your partner know how you’re feeling about the diagnosis and emphasize your commitment to managing the condition.
- Be open to questions: Listen attentively to your partner’s concerns and answer their questions honestly.
- Practice safe sex: Consistent and correct condom use can significantly reduce the risk of transmission during outbreaks. There are also antiviral medications that can further decrease the risk of transmission.
The Future of Herpes Research
Researchers are constantly striving to develop new and improved treatment options for herpes. This includes exploring the potential for a vaccine to prevent future infections and even a cure to eradicate the virus entirely. While such advancements might still be some time away, ongoing research offers a ray of hope for the future.
Conclusion
Herpes, while a common STI, can be effectively managed with proper diagnosis, treatment, and self-care. By understanding the different types of herpes, their symptoms, and available management strategies, you can take control of your health and maintain a fulfilling quality of life. Remember, open communication with healthcare providers and sexual partners is essential for navigating herpes and building healthy relationships.